45 labeling nucleotide examples
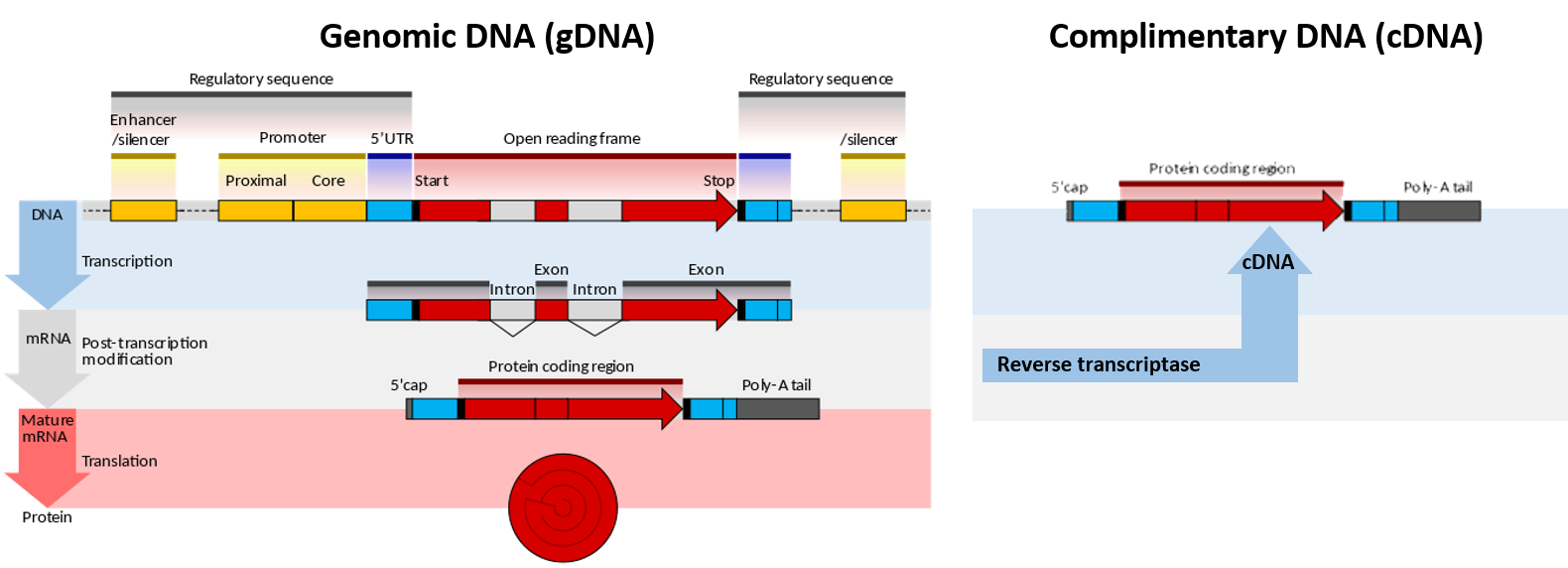
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific - DE 1. 5′ end-labeled primers can be used with this method in order to add a 5′ modification to a DNA probe. · 2. Modified nucleotides can be added to the 3′ ... A Simple Method for 3′-Labeling of RNA - Oxford Academic We have described a simple procedure by which the 3′-termini of RNA molecules can be labeled by using the Klenow fragment of E.coli DNA polymerase I to extend the 3′-end of the RNA by one nucleotide on a short complementary DNA template.
Labeled Nucleotides | Biocompare 2579 products ... Labeled nucleotides are available from several suppliers for use in molecular biology. These nucleoside triphosphates, conjugated to moieties ...

Labeling nucleotide examples
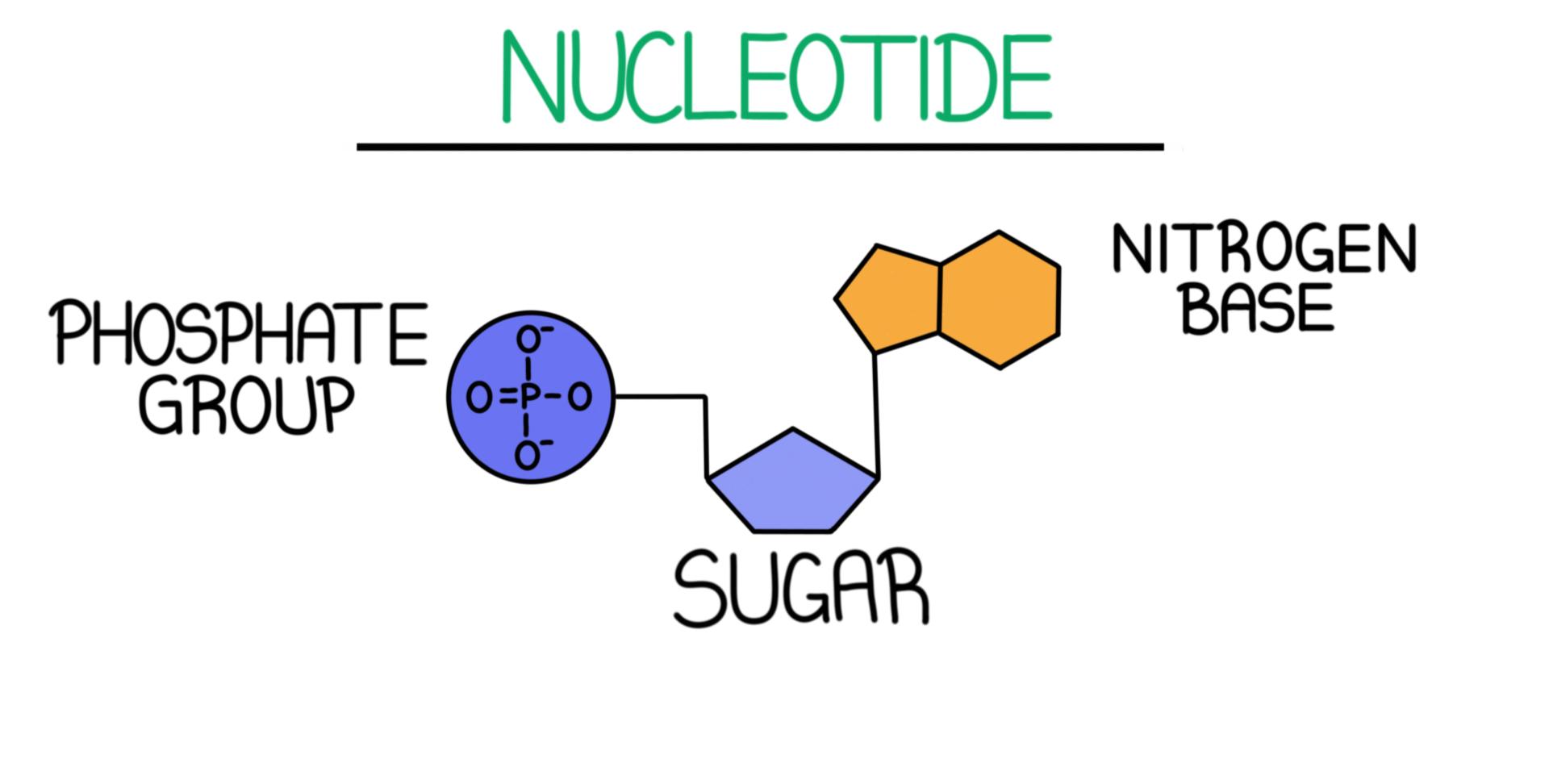
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides perform several important functions in the human body in free state as well as a component of nucleic acids. For example, ATP is a nucleotide that acts as energy currency of a cell. GDP and GTP are nucleotides essential for cell signaling. NAD is a dinucleotide that acts as a coenzyme in various metabolic reactions. DNA sequencing (article) | Biotechnology | Khan Academy DNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotide bases (As, Ts, Cs, and Gs) in a piece of DNA. Today, with the right equipment and materials, sequencing a short piece of DNA is relatively straightforward. Sequencing an entire genome (all of an organism's DNA) remains a complex task. It requires breaking the DNA of the ... Nucleic acids (article) | Khan Academy Each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a nitrogen-containing ring structure called a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and at least one phosphate group. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. ... For example ...
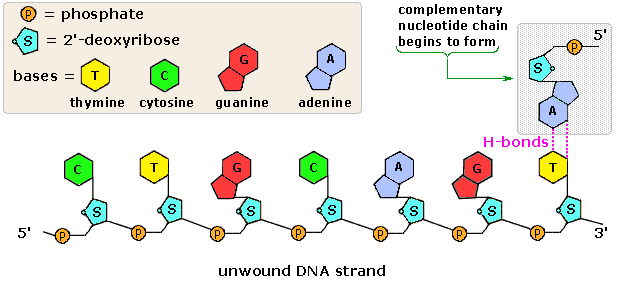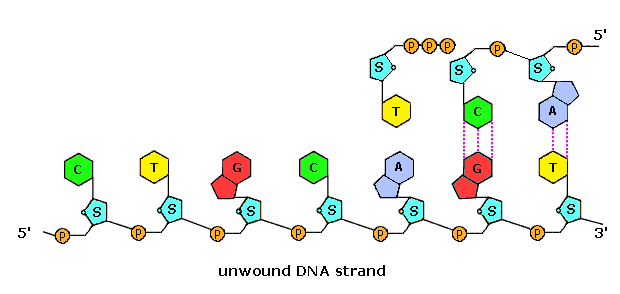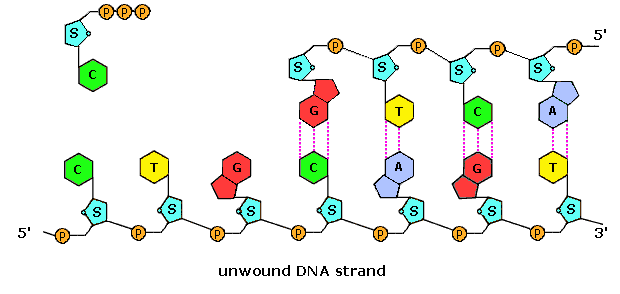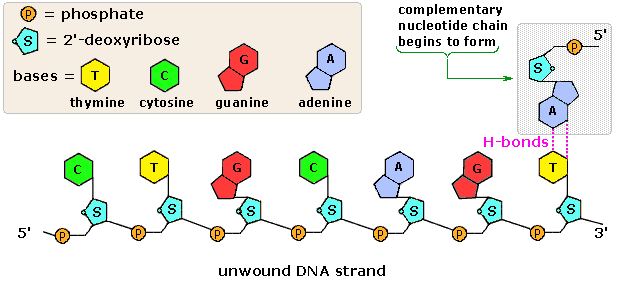
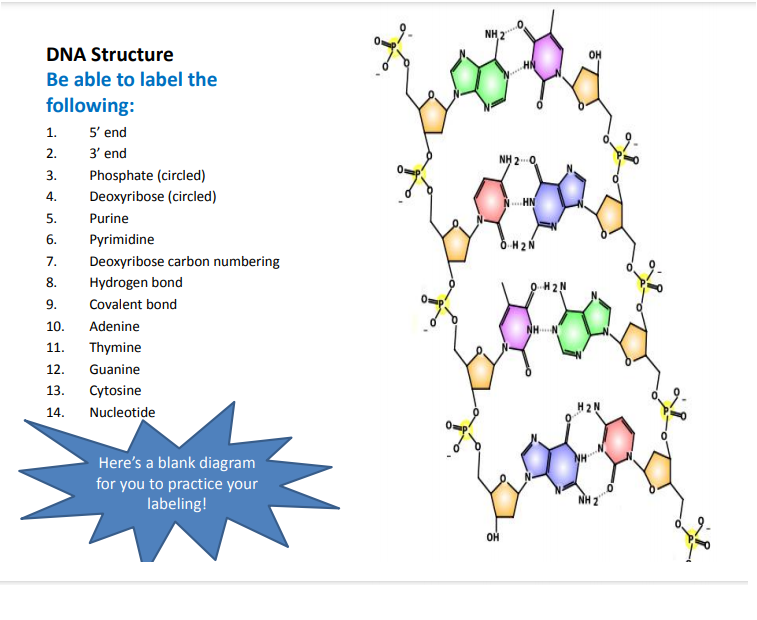
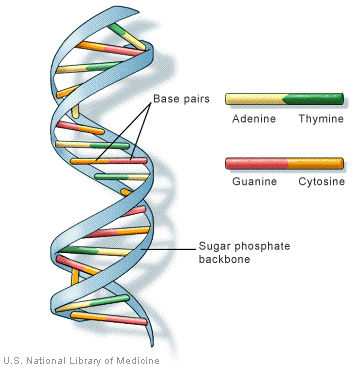
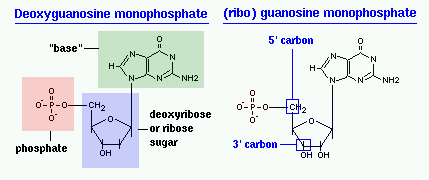
Labeling nucleotide examples. The genetic code & codon table (article) | Khan Academy Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Here are some features of codons: Most codons specify an amino acid Three "stop" codons mark the end of a protein One "start" codon, AUG, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine Nucleic Acid Labeling - Sepmag The type of nucleotide is based on the type of nitrogenous base that is bound. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) the four predominantly found ... Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Nucleotide Examples Adenine Adenine is a purine, which is one of two families of nitrogenous bases. Purines have a double-ringed structure. In DNA, adenine bonds with thymine. In RNA, adenine bonds with uracil. Adenosine triphosphate, as discussed earlier, uses the nucleotide adenine as a base. From there, three phosphate groups can be attached. 2.6: DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet Identify and label carbons by number (for example, C1, C2, C3) on a nucleotide drawing. Understanding: The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. The carbons of the sugar component of the nucleotide are numbers clockwise, starting from the oxygen in the ring at the top and the phosphate group to the left.
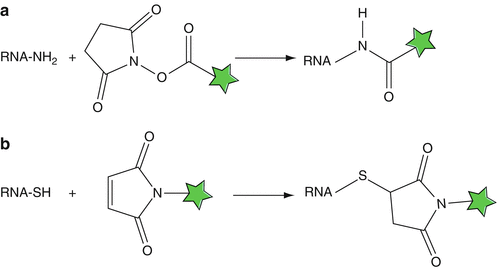
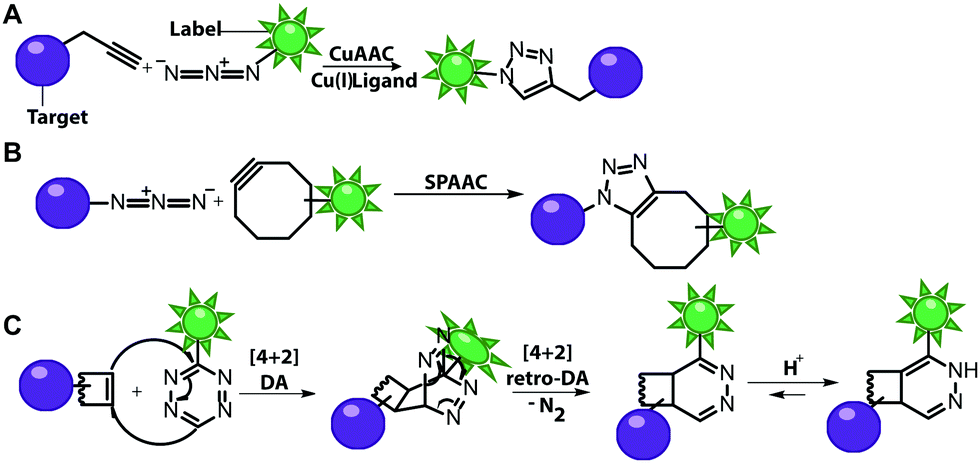
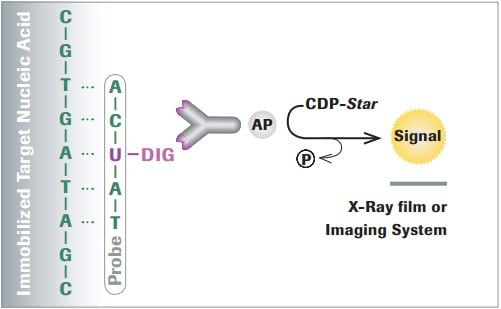
Metabolic Labeling Strategies - Thermo Fisher Scientific Protein Biology Resource Library. Pierce Protein Methods. Metabolic labeling refers to methods in which the endogenous synthesis and modification machinery of living cells is used to incorporate detection or affinity tags into biomolecules. Typically, this is accomplished by culturing cells or organisms in media in which a specific natural ... PDF Non-Radioactive Nucleic Acid Labeling and Detection in the form of a biotinylated nucleotide by enzymatic methods. (Details of each labeling method described in Chapter 2)Biotin may also be attached by direct means using intercalation or photo-activatable groups. Biotinylation rarely interferes with biological activity, and linker arms between the biotin and the probe minimize steric interference. Covalent labeling of nucleic acids - RSC Publishing Both SPAAC and IEDDA reactions have also been used for covalent labeling of nucleic acids as many examples in this review will illustrate. ... To this end, a single stranded 19-mer DNA bearing one dC Trp nucleotide was synthesized and the fluorescence emission was detected in absence and presence of single-strand binding protein from E. coli ... DNA Labeling - New England Biolabs - NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified ...
US6338943B1 - Methods for labeling nucleotides ... - Google Patents Further, Gebeyehu et al., Nucleic Acids Research, 15, (1987), 4513-4534, have reported that adenine and cytosine may be labeled with biotin derivatives through ... Nucleotide and structural label identification in single RNA ... - NCBI Traditional methods of biomolecular structure determination, such as X-ray crystallography7 and NMR,8 require considerable sample preparation, ... Nucleotide - National Human Genome Research Institute Definition 00:00 00:44 A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Radioisotope labeling: Considered as a conventional method for nucleic acid labeling, radiolabeled nucleotides are synthesized using ATP-gamma- ...
Nucleotides labeled with... - Jena Bioscience Nucleotides labeled with... · Adenosines · Guanosines · Cytidines · Uridines · Thymidines · Xanthosines · Inosines.
Structure of Nucleic Acids | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose (five-carbon) sugar, and a phosphate group (Figure 1). Each nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is attached to a sugar molecule, which is attached to one or more phosphate groups. ... For example, a certain purine can only pair with a certain pyrimidine. This means A can ...
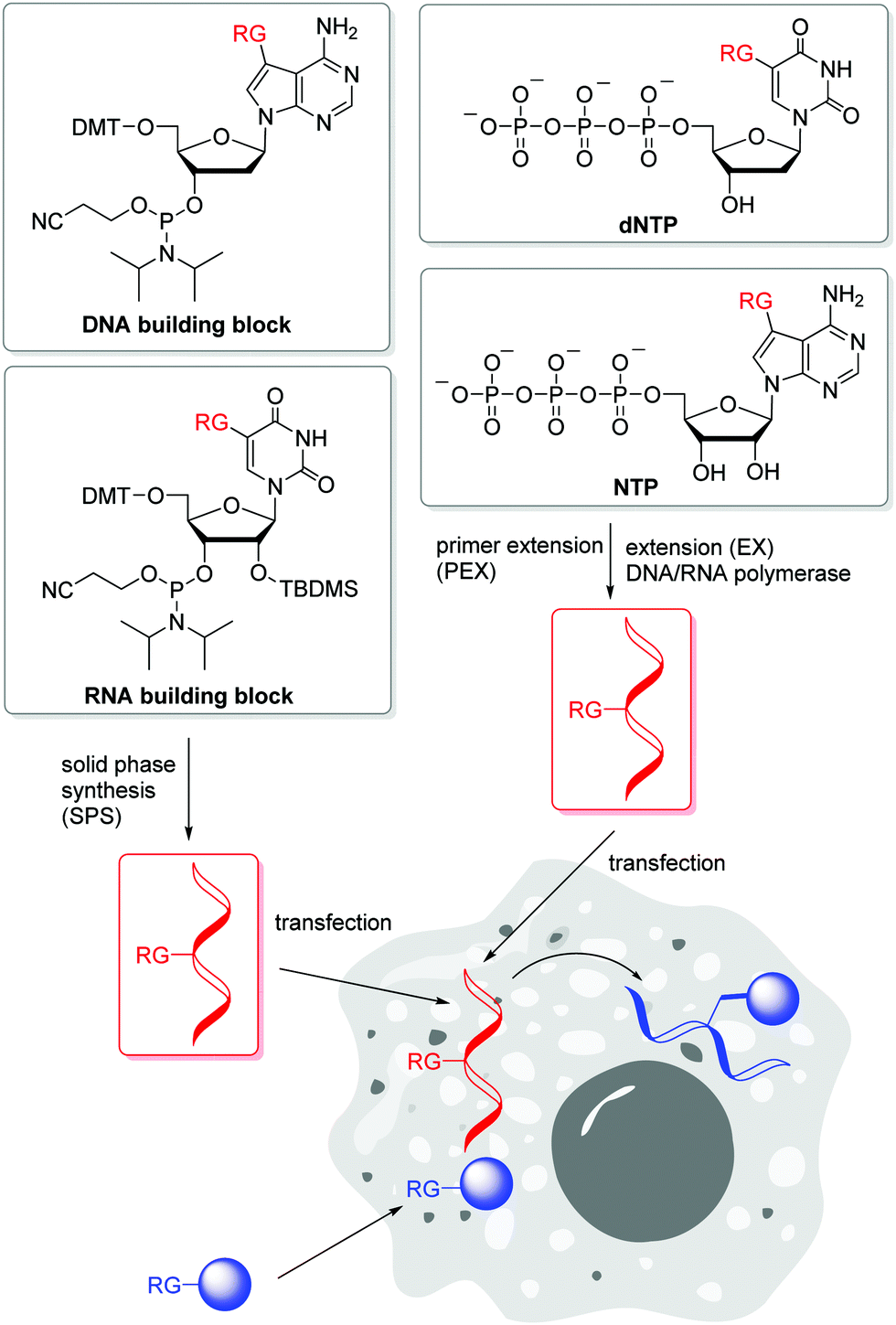
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 The aminoalkynyl linker between the fluorophore and the nucleotide in the ChromaTide UTP and dUTP nucleotides is designed to reduce the fluorophore's interaction with enzymes or target binding sites. ... nucleotides or with commercially available aminoallyl nucleotide-based nucleic acid labeling kits. With excitation/emission maxima of 495/ ...
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Radioactive tracer - Wikipedia For example, 13 C + n → 14 C In this case the atomic mass increases, but the element is unchanged. In other cases the product nucleus is unstable and decays, typically emitting protons, electrons ( beta particle) or alpha particles. When a nucleus loses a proton the atomic number decreases by 1. For example, 32 S + n → 32 P + p
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes. In addition, the bioconjugation methods used for nucleic acid probe generation may be adapted for attaching nucleic acids to other molecules or surfaces to facilitate targeted delivery or immobilization, respectively. Page contents
dna-labeling | NEB DNA Labeling. Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end ...
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Radiolabeled nucleotides are commonly used for detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. They are typically incorporated enzymatically into DNA and RNA ...
DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new DNA strands. A replication unit is any chunk of DNA that is capable of being replicated — e.g. a plasmid with an origin of replication (ORI) is a replication unit. Alternatively, this can also mean a region of DNA that is replicated together.
Nucleic Acid Labeling | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Fluorescently labeled nucleotides Oligo Labeling & Synthesis Create optimally fluorescence-labeled, biotin-labeled, or radiolabeled oligonucleotides with these oligonucleotide labeling kits and enzymes. Ulysis Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits ( Alexa Fluor 488, Alexa Fluor 596, Alexa Fluor 594, Ulysis Alexa Fluor 647)
PDF Oligonucleotide 3' End Labeling 1. Introduction - PerkinElmer nucleotide analogs which lack a 3' hydroxyl are used (NEG026), the result is that a single nucleotide is added to the 3' end of the nucleic acid. Labeling of the 3' end using 2'deoxynucleotides results in a polymeric tail ("tailing" - the addition of multiple labeled nucleotides at the end of the oligo). The
Nucleic acids (article) | Khan Academy Each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a nitrogen-containing ring structure called a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and at least one phosphate group. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. ... For example ...
DNA sequencing (article) | Biotechnology | Khan Academy DNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotide bases (As, Ts, Cs, and Gs) in a piece of DNA. Today, with the right equipment and materials, sequencing a short piece of DNA is relatively straightforward. Sequencing an entire genome (all of an organism's DNA) remains a complex task. It requires breaking the DNA of the ...
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides perform several important functions in the human body in free state as well as a component of nucleic acids. For example, ATP is a nucleotide that acts as energy currency of a cell. GDP and GTP are nucleotides essential for cell signaling. NAD is a dinucleotide that acts as a coenzyme in various metabolic reactions.








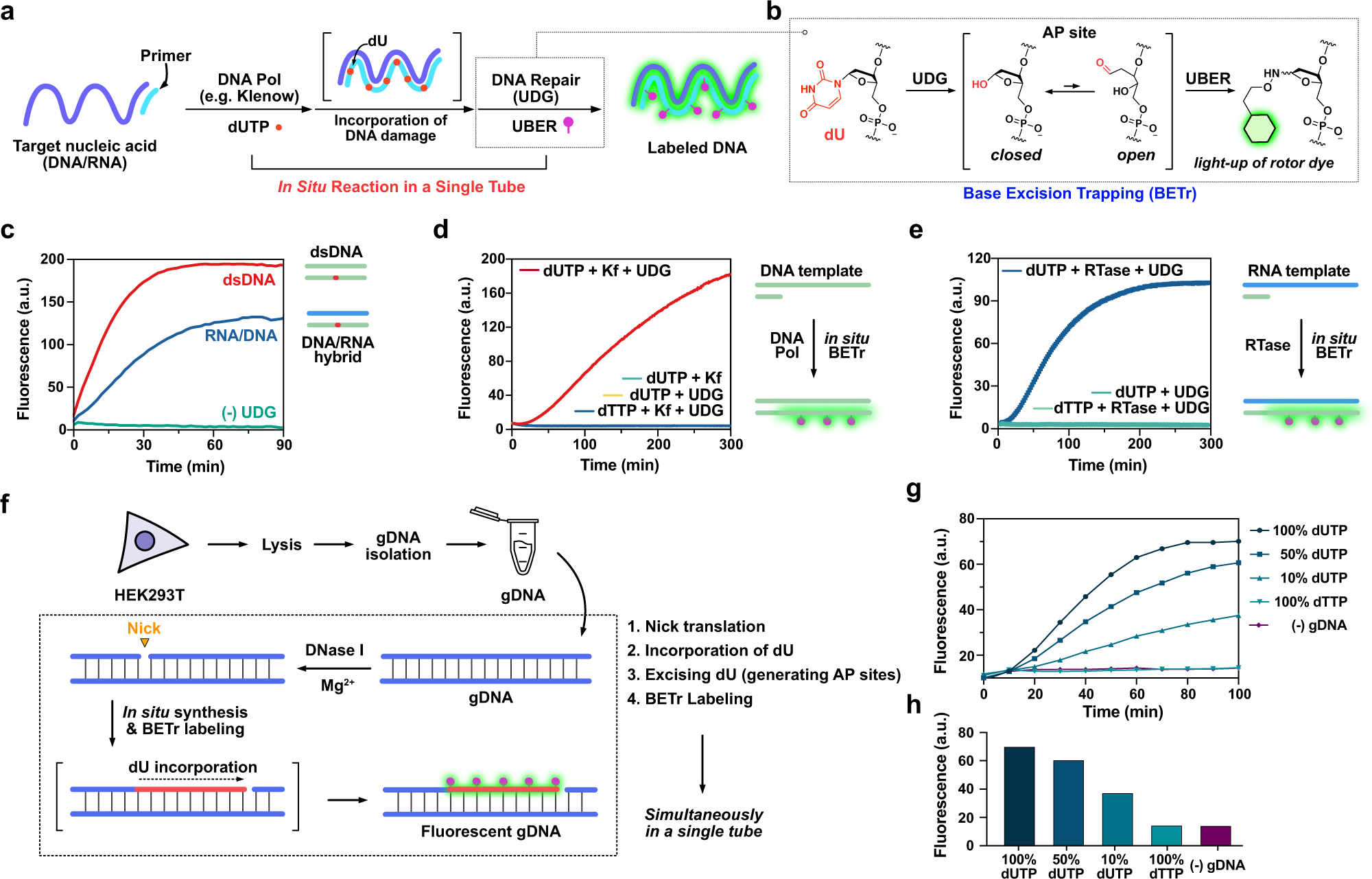
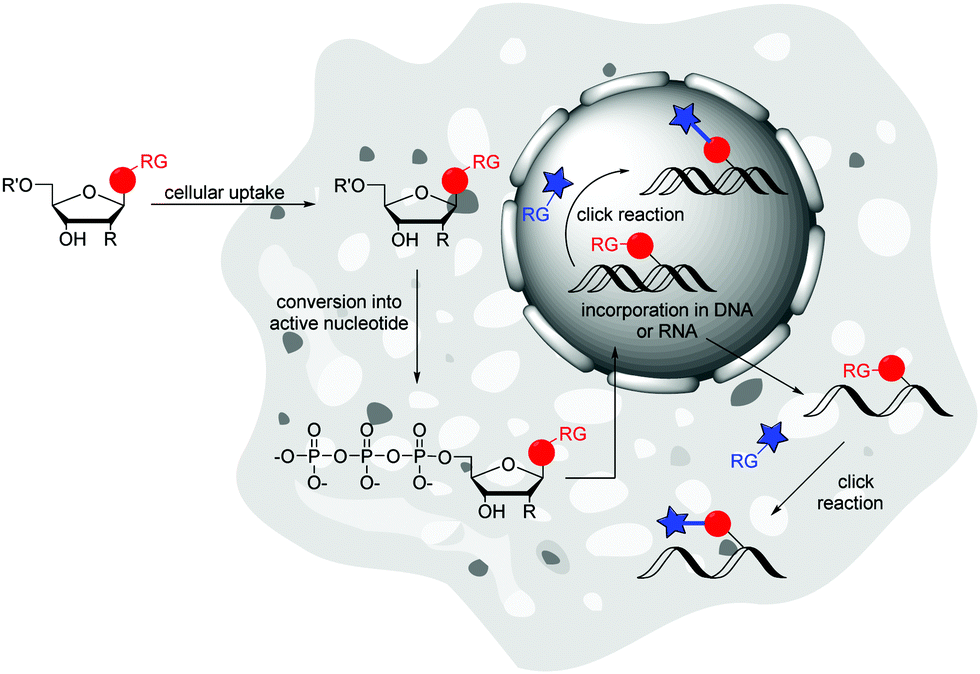










![PDF] Analytical ancestry:](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/faf60b0846345f8087f4044ad5af606ccc54d68e/4-Figure2-1.png)






Post a Comment for "45 labeling nucleotide examples"